Pakistan Crypto Market: $25B Digital Assets Make It 8th Largest Globally
Pakistan's crypto market ranks 8th globally with $25 billion in digital assets. ADB report reveals explosive growth in Pakistan's cryptocurrency adoption.
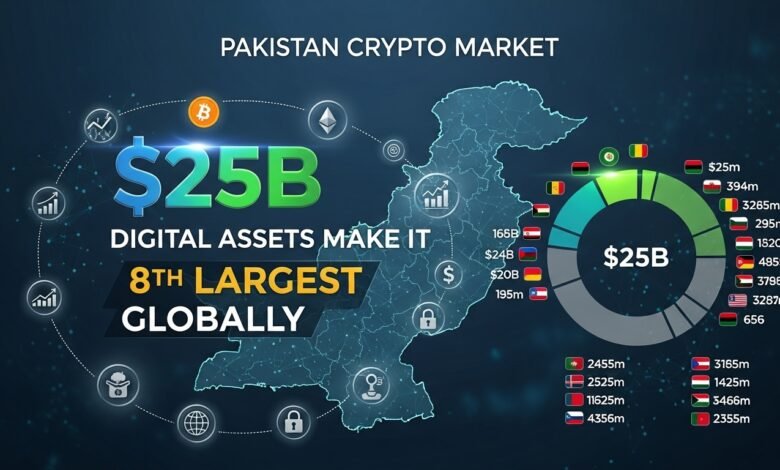
Pakistan’s crypto market digital assets have surged to an astounding $25 billion valuation, catapulting the nation to become the eighth-largest cryptocurrency market globally. This remarkable achievement positions Pakistan ahead of several developed economies and signals a fundamental shift in how financial technology is reshaping economic participation across the developing world.
The significance of this development extends far beyond mere statistics. For a nation grappling with economic challenges, currency devaluation, and banking accessibility issues, the explosive growth of the Pakistan crypto market represents both an opportunity and a paradigm shift in how millions of citizens engage with modern financial instruments. The ADB’s comprehensive analysis has illuminated patterns of adoption that reveal cryptocurrency is no longer a niche interest reserved for tech enthusiasts but has become a mainstream financial tool for ordinary Pakistanis seeking economic empowerment and financial inclusion.
Scale: What $25 Billion in Digital Assets Really Means
When examining the magnitude of Pakistan’s crypto market digital assets, the $25 billion figure deserves contextual analysis to appreciate its true significance. This valuation encompasses a diverse ecosystem of digital assets, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, stablecoins, and various altcoins that Pakistani investors have accumulated through peer-to-peer platforms, international exchanges, and local trading networks. The figure represents not just speculative investment but also remittances, international trade settlements, and increasingly, everyday financial transactions that bypass traditional banking infrastructure.
The Asian Development Bank’s methodology for calculating this valuation incorporated data from blockchain analytics firms, exchange volume tracking, and on-chain transaction analysis specific to Pakistani wallets and trading patterns. What emerges from this data is a portrait of unprecedented retail participation in cryptocurrency markets, with estimates suggesting that between eight to twelve million Pakistanis actively engage with digital currency platforms in some capacity. This level of penetration is extraordinary when compared to Pakistan’s traditional banking sector, where financial inclusion has historically lagged behind regional competitors.
The composition of these $25 billion in digital assets reveals interesting preferences among Pakistani investors. Bitcoin remains the dominant cryptocurrency, commanding approximately forty percent of the total market share, followed by USDT and other stablecoins that serve crucial functions in preserving value against rupee volatility. Ethereum and its associated decentralized finance ecosystem account for another significant portion, while emerging layer-one blockchains and localized crypto projects have begun capturing market share among more sophisticated investors.
The Drivers Behind Pakistan’s Cryptocurrency Boom
Multiple converging factors have propelled the Pakistan crypto market to its current prominence on the global stage. Economic uncertainty has served as perhaps the most powerful catalyst, with the Pakistani rupee experiencing significant devaluation against major currencies over recent years. This erosion of purchasing power has driven citizens toward alternative stores of value, with cryptocurrencies offering both accessibility and the potential for appreciation that traditional savings vehicles cannot match.
Banking sector limitations have created fertile ground for cryptocurrency adoption. Pakistan’s formal banking system reaches only a fraction of the population, with millions of citizens lacking access to basic financial services. Cryptocurrency platforms require only a smartphone and internet connection, democratizing access to financial tools previously available only to the banked elite. This technological leapfrogging mirrors patterns seen with mobile phone adoption in developing markets, where emerging technologies bypass inadequate traditional infrastructure entirely.
The remittance economy has played an instrumental role in driving crypto adoption in Pakistan. As one of the world’s largest recipients of worker remittances, Pakistan sees billions of dollars flowing from expatriate workers annually. Traditional remittance channels impose substantial fees and delays, whereas cryptocurrency transfers offer near-instantaneous settlement at fractional costs. This practical utility has transformed how many Pakistani families receive international transfers, with stablecoins becoming a preferred medium for cross-border payments.
Youth demographics constitute another critical factor. Pakistan boasts one of the world’s youngest populations, with a median age under twenty-three years. This demographic cohort demonstrates remarkable comfort with digital technologies and has embraced cryptocurrencies with enthusiasm unmatched by older generations. Social media platforms have facilitated knowledge sharing about crypto trading strategies, investment opportunities, and blockchain technology fundamentals, creating viral adoption patterns that have accelerated market growth exponentially.
Regulatory Landscape: Navigating Uncertainty in Pakistan’s Crypto Ecosystem
The regulatory environment surrounding the Pakistan crypto market digital assets remains complex and somewhat contradictory. The State Bank of Pakistan has maintained an officially cautious stance, issuing periodic warnings about the risks associated with cryptocurrency trading while stopping short of implementing comprehensive bans. This ambiguous position has created a gray zone where cryptocurrency activity flourishes despite the absence of clear legal frameworks or consumer protections.
Recent developments suggest a gradual evolution toward more structured regulation. Government officials have increasingly acknowledged the impossibility of preventing cryptocurrency adoption through prohibition, particularly given the decentralized nature of blockchain networks and the ease with which citizens can access international trading platforms. Instead, discussions have shifted toward frameworks that might bring crypto trading within regulatory purview while protecting investors and preventing illicit financial flows.
The Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf government initiated exploratory conversations with international regulatory bodies and cryptocurrency experts to develop appropriate oversight mechanisms. Proposals under consideration include licensing requirements for domestic cryptocurrency exchanges, taxation frameworks for digital asset gains, and anti-money laundering compliance standards adapted to blockchain transactions. However, implementation has proceeded slowly, reflecting both technical capacity constraints and ongoing debates about the appropriate balance between innovation and consumer protection.
This regulatory uncertainty creates both opportunities and risks for participants in the Pakistan digital currency market. The absence of clear rules has allowed entrepreneurial innovation to flourish without bureaucratic constraints, enabling rapid experimentation with new business models and financial products. Conversely, investors lack legal recourse when disputes arise, and the potential for fraud or market manipulation remains elevated compared to regulated financial markets.
Economic Implications: How Cryptocurrency is Reshaping Pakistan’s Financial Landscape
The emergence of Pakistan as a major crypto market carries profound implications for the nation’s broader economic trajectory. At the microeconomic level, cryptocurrency access has provided millions of previously unbanked citizens with tools for wealth preservation, investment, and participation in global financial markets. This financial inclusion dimension cannot be overstated, as it represents a democratization of economic opportunity previously unavailable to large segments of Pakistani society.
Cryptocurrency’s role in facilitating international trade and commerce has grown substantially. Pakistani businesses engaged in import-export activities increasingly utilize digital assets to settle cross-border transactions, circumventing currency conversion fees and delays associated with traditional banking channels. This efficiency gain has particular relevance for small and medium enterprises that lack the relationships and credit facilities that larger corporations enjoy with international banks.
The $25 billion valuation of Pakistan’s crypto holdings represents significant capital that might otherwise have fled the country entirely or remained idle in physical assets like gold or real estate. While volatility concerns remain valid, the liquidity and divisibility of cryptocurrencies make them superior to many traditional stores of value for ordinary citizens. This capital formation, even in digital form, contributes to economic dynamism and provides investment resources that can be deployed as market conditions evolve.
Employment generation through the cryptocurrency ecosystem has become increasingly significant. The Pakistan crypto market has spawned an entire industry of traders, educators, content creators, peer-to-peer facilitators, and technical service providers. Blockchain developer roles have multiplied, with Pakistani programmers increasingly sought after in international markets for their skills in smart contract development, decentralized application creation, and blockchain security auditing.
Pakistan’s Position Among the World’s Largest Crypto Markets
Pakistan’s ranking as the eighth-largest crypto market globally places it in distinguished company, ahead of several developed economies with far higher per capita incomes and more established financial infrastructure. This positioning reflects the unique dynamics of cryptocurrency adoption, which often shows inverse correlation with traditional financial system development. Nations with robust banking sectors and stable currencies frequently exhibit lower cryptocurrency adoption rates, while emerging markets facing currency instability and banking access challenges demonstrate explosive growth.
Comparing Pakistan’s crypto market with regional neighbors reveals interesting patterns. India, despite a larger economy and population, has faced more restrictive regulatory approaches that have potentially constrained market development. Bangladesh has implemented more aggressive cryptocurrency prohibitions, while Afghanistan’s collapsed financial system has driven desperate citizens toward digital alternatives. Pakistan’s relatively permissive regulatory stance, whether intentional or through inaction, has allowed market forces to drive adoption organically.
The composition of global cryptocurrency markets shows fascinating disparities. While developed markets exhibit higher absolute values concentrated among institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals, emerging markets like Pakistan demonstrate broader retail participation with smaller individual holdings aggregating to substantial totals. This grassroots adoption pattern suggests greater resilience and potentially more sustainable long-term growth trajectories compared to markets dependent on institutional flows that can reverse suddenly.
Technological Infrastructure: Building the Foundation for Crypto Adoption
The rapid expansion of the Pakistan crypto market digital assets would be impossible without corresponding developments in technological infrastructure. Internet penetration has reached approximately fifty percent of the population, with 4G mobile networks now covering most urban and semi-urban areas. This connectivity provides the essential foundation for cryptocurrency wallet access, trading platform utilization, and blockchain network participation.
Smartphone adoption has proven particularly crucial. Pakistan’s mobile phone market has experienced remarkable growth, with affordable Android devices bringing computing power to citizens across all economic strata. These devices serve as the primary interface for crypto trading, with mobile applications from international exchanges and local peer-to-peer platforms optimized for Pakistani users. The smartphone-first nature of Pakistan’s digital economy has shaped cryptocurrency adoption patterns, with mobile-native solutions achieving far greater traction than desktop-based platforms.
Payment infrastructure developments have facilitated fiat-to-crypto on-ramps and off-ramps essential for market liquidity. While Pakistani banks officially discourage cryptocurrency transactions, peer-to-peer networks have evolved sophisticated systems for fiat conversion using traditional payment methods including bank transfers, mobile wallets, and even cash transactions. These informal but highly efficient networks have proven remarkably resilient, adapting quickly to regulatory pressures and technological changes.
Blockchain education initiatives have proliferated across Pakistan’s major cities, with universities, private academies, and online learning platforms offering courses in cryptocurrency fundamentals, trading strategies, and blockchain development. This knowledge infrastructure supports sustainable market growth by creating informed participants who understand both the opportunities and risks inherent in digital asset investments. Community-driven education through social media groups, YouTube channels, and messaging apps has democratized access to trading knowledge previously available only to financial professionals.
Risk Factors and Challenges Facing Pakistan’s Crypto Market
Despite impressive growth metrics, the Pakistan crypto market faces substantial challenges that could impede future development or expose participants to significant losses. Market volatility remains the most immediate concern, with cryptocurrency prices subject to dramatic fluctuations that can devastate unprepared investors. The lack of investor education among many participants means substantial portions of the $25 billion in holdings belong to individuals who may not fully understand the risks they have assumed.
Cybersecurity threats pose existential risks to market participants. Pakistan’s cryptocurrency ecosystem operates largely through international platforms and local peer-to-peer networks, many lacking robust security protocols. Phishing attacks, exchange hacks, and social engineering scams have cost Pakistani investors millions of dollars, with victims having little recourse due to the unregulated nature of most platforms. The absence of deposit insurance or consumer protection mechanisms means losses are typically permanent and unrecoverable.
Regulatory risk represents an ongoing concern despite current permissive conditions. Government policy could shift dramatically in response to perceived threats, international pressure, or financial sector lobbying. Comprehensive prohibition, while difficult to enforce, could drive the market underground, eliminate legitimate business operations, and expose participants to criminal liability. Even well-intentioned regulation could have chilling effects if poorly designed or implemented without adequate consultation with market participants.
Infrastructure reliability challenges persist despite improvements in connectivity. Power outages, internet disruptions, and payment system failures can temporarily freeze market access during critical periods, preventing traders from responding to price movements or managing risk positions. These infrastructure gaps create asymmetries where better-resourced participants with backup systems and redundant connectivity enjoy substantial advantages over ordinary retail investors.
The Future Trajectory: Where Pakistan’s Crypto Market is Headed
Projecting the future development of the Pakistan crypto market requires considering multiple scenarios ranging from explosive continued growth to regulatory crackdowns. The most probable path involves gradual institutionalization, with regulatory frameworks emerging that provide legitimacy and consumer protection while preserving the innovation and accessibility that have driven adoption. This evolution would likely mirror patterns observed in other emerging markets that have successfully integrated cryptocurrencies into their financial ecosystems.
Technological advancement will continue to reshape the market landscape. Second-layer scaling solutions, central bank digital currency developments, and improved cross-chain interoperability will enhance the utility and efficiency of cryptocurrency platforms serving Pakistani users. These technical improvements could expand use cases beyond speculative trading toward everyday commerce, remittances, and even government service delivery.
Institutional participation represents a potential game-changer for market maturity. If Pakistani financial institutions begin offering cryptocurrency custody services, investment products, or trading facilities, it would signal mainstream acceptance and potentially attract capital from conservative investors currently sidelined by regulatory uncertainty. However, this institutionalization could also transform market dynamics, potentially reducing the accessibility and democratization that have characterized Pakistan’s grassroots crypto adoption.
International integration will likely deepen as Pakistani cryptocurrency users increasingly participate in global decentralized finance protocols, non-fungible token markets, and cross-border blockchain applications. This global connectivity could position Pakistan as a significant player in the emerging digital economy, with Pakistani developers, traders, and entrepreneurs contributing to worldwide blockchain innovation while earning foreign exchange and developing valuable technical expertise.
Conclusion
The revelation that the Pakistan crypto market digital assets have reached $25 billion, establishing the nation as the eighth-largest crypto market globally, represents far more than a statistical curiosity. This development signals a fundamental transformation in how millions of Pakistanis interact with financial systems, preserve wealth, and participate in the global digital economy. The Asian Development Bank’s findings validate what observers have witnessed organically—a grassroots financial revolution driven by economic necessity, technological accessibility, and entrepreneurial innovation.
As Pakistan navigates the complexities of integrating cryptocurrency into its economic fabric, balanced approaches that protect consumers while fostering innovation will prove essential. The potential benefits—financial inclusion, remittance efficiency, capital formation, and technological development—justify thoughtful engagement rather than prohibitionist reactions. The Pakistan digital currency market has demonstrated remarkable resilience and growth despite operating in regulatory gray zones; imagine the possibilities if provided with clear rules, consumer protections, and institutional support.
For investors, entrepreneurs, policymakers, and ordinary citizens, understanding the dynamics of Pakistan’s cryptocurrency ecosystem has never been more important. Whether you are considering participating in the Pakistan crypto market, developing blockchain applications, or simply seeking to understand this financial phenomenon, now is the time to engage with this transformative technology. The $25 billion in digital assets held by Pakistanis represents not just wealth but also hope, innovation, and the possibility of a more inclusive financial future.
See more: Tether Gold Reserve Switzerland: Massive Crypto-Backed Assets